Light creates understanding, understanding creates love, love creates patience, and patience creates unity
Malcolm X
The efficacy from analyze to execution of an automated test is required to conceptualize design and execute successfully the test. In this article I propose a guideline to accomplish the challenge to create an automated test.
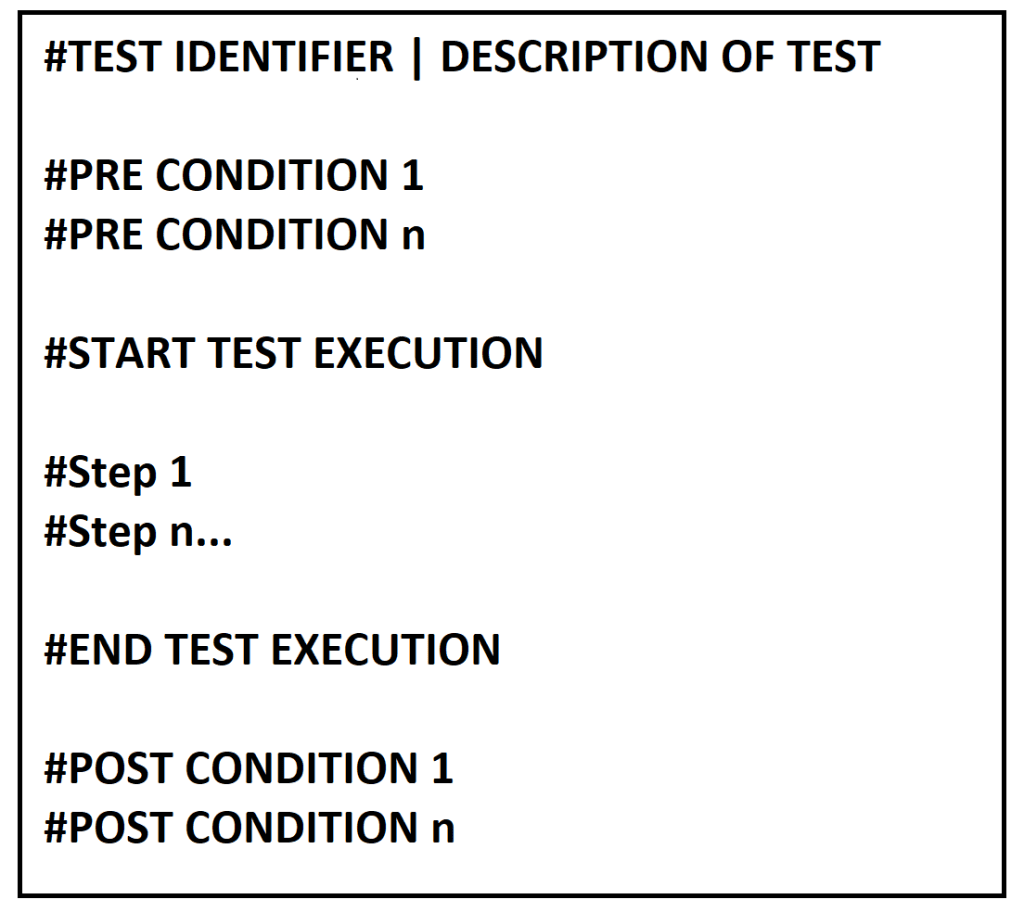
Life cycle of the test
The list of business or technical requirements, describe the expectations of the system with a certain degree of precision or not. A tester, another stakeholders and process involved on the application life cycle will clarify this list of requirements.
Requirements will certainly evolve in time, the symbiosis between test and requirements will define the validity and pertinence of the test and provide more degraded test cases. Test must always be aligned with a unique business-goal or technical-goal (atomic principle of test), and keep on mind the add value of your test for the client or design of your software. Translate in a simple sentence using the same jargon of your client. This concept is independent of any technical implementation, so forget (at this point) the nature (manual or automated) of the execution of test.
First : Try to execute it manually
Try to execute and re-execute manually the test to be sure that you understand the procedure to execute the test. At this point some issues should be revealed :
- Which pre conditions are required to execute the test?
- It is an atomic test? Each test must be independent from another test
- It is repeatable?
- It is “fast”?
- Write down input/output required
- Is the system to test stable?
- Post conditions are required?
- Note : What if is an API test? try to use some tools to reproduce the code, for instance : Postman, or another similar tool
Test Anatomy
Technically the structure of test can be different in function of the technology used, the representation must have the same topology. I write down this in pseudo-code
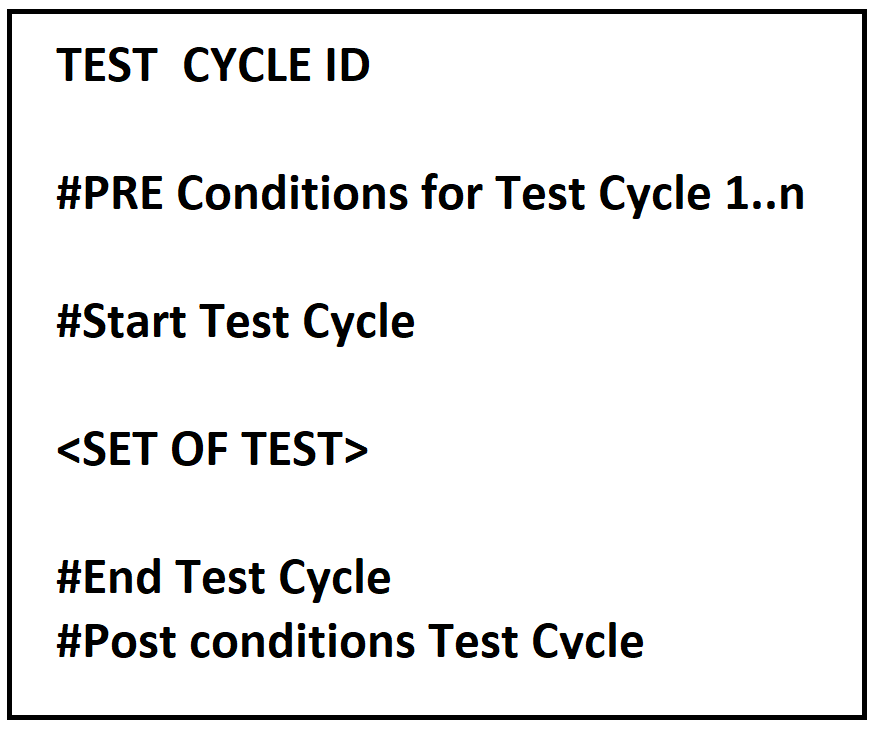
In the same logic, a test belongs to another set of test : Test Cycle. The patter can be applied also for each set of test
Tips
- Identify the factors that could break you automated test and you can not control : change of layout in interface, malfunctioning device, internet off, network issues,DB offline, API backend off etc.No silver bullet to solve these issues. Isolate the issues and propose technical solutions that can be described in the preconditions.
- Precondition on Test Cycle : Validate that all the conditions are ready to start the execution of the test cycle. For example, setup server, configuration, etc
- Precondition on Test Cycle: Execute a sanity check about the graphic elements that the APP must have.
- Precondition on Test Cycle: Execute integration and unit test of your ow test framework
- Preconditions on Test And / Or Test Cycle : Mock or create virtual services that test can control.
- Test centered on business goal/technical goal. Reduce the intermediate points or interfaces that are not part of test. If you are testing a “Shopping cart” and the business goal is verify that if you change the quantity of items the price to pay must be updated, don’t waste your time in the ‘previous’ steps : open a session, browse a category, select different items, and finally test your “shopping car”. This kind of test is designed to fail. Try another strategy :
- Precondition on test : Inject in the DB / Backend the items chosen.
- Another option : Mock your DB or Backend
- Precondition on test : Create a login session programatically to avoid the login process
- Precondition on test : Create a link to “redirect” the test directly to the “Shopping car”
- Precondition on test : Inject in the DB / Backend the items chosen.
- Like I wrote in a previous article, the test must be “clustered” with test with the same functional axis.
